Dimitris Tzionas
Guest Scientist
Max-Planck-Ring 4
72076 Tübingen
Germany
Welcome to my homepage!
I am an Assistant Professor at the University of Amsterdam (UvA) since June 2022.
I have migrated to https://dtzionas.com but, for now, I still update this webpage (i.e. both webpages).
--- Motivated students can contact me by following these instructions (my email: d.tzionas@uva.nl).
Earlier I was a Research Scientist at the Perceiving Systems (PS) department of Michael Black, at MPI for Intelligent Systems in Tübingen.
Even earlier I was a PostDoc at PS. I received a PhD from the University of Bonn for my work with Juergen Gall on Hand-Object Interaction.
My alma mater is the Aristotle University of Thessaloniki in Greece, where I studied Electrical and Computer Engineering, and I closely cooparated with Leontios Hadjileontiadis.
Research Direction
I conduct research on the intersection of Computer Vision (CV), Computer Graphics (CG) and Machine Learning (ML). My motivation is to understand and model how people look, move and interact with the physical world and with each other to perform tasks.
This involves (1) accurately "capturing" real people and their whole-body interactions with scenes and objects, (2) modeling their shape, pose and interaction relationships, (3) applying these models to reconstruct real-life actions in 3D/4D, and (4) using these models to generate realistic interacting avatars in 3D/4D.
Potential applications include Ambient Intelligence, Virtual Assistants, Human-Computer/Robot Interaction, Augmented/Virtual Reality (AR/VR) and the "Metaverse".
The long-term goal is to develop human-centered AI that perceives humans, understands their behavior and helps them to achieve their goals.
News in a Nutshell
Jan 2024: Accepted paper at IJCV (special issue) - InterCap. Congrats Yinghao et al.!
Dec 2023: George Paschalidis starts his PhD -- welcome on board!
Dec 2023: Accepted CVPR'24 workshop: The 2nd Rhobin challenge (co-organizer with a great group of colleagues).
Oct 2023: Accepted papers at 3DV 2024: POCO (congrats Sai et al.!) and GRIP (congrats Omid et al.!)
Sep 2023: I serve as an Area Chair for 3DV 2024.
Aug 2023: Two BSc theses and a MSc thesis submitted (UvA). Congrats Benjamin, Roan & Romana!
July 2023: Open PhD position at the UvA (Deadine is over).
July 2023: Accepted paper at ICCV 2023: DECO (website coming soon) -- congrats Shashank et al.!
Jun 2023: Guest lecture (1h) on 3D perception of humans at UvA's "Computer Vision II" course.
May 2023: Outstanding Reviewer award for CVPR 2023 (top 3.5%).
April 2023: Congrats to Shashank & Omid for their distinctions in the Meta 2023 fellowship program!
Mar 2023: Dimitrije Antic starts his PhD -- welcome on board!
Feb 2023: Accepted papers at CVPR 2023: HOT (congrats Yixin et al.!), IPMAN (congrats Shashank et al.!), ECON (congrats Yuliang et al.!), ARCTIC (congrats Alex et al.!), and SGNify (congrats Paola et al.!).
Feb 2023: The New York Times (NYT) uses our ICON software in an interactive article for reconstructing key goals at the 2023 Super Bowl (American football league).
Dec 2022: Congratulations to Dr. Choutas for a successful PhD defence!
Nov 2022: The New York Times (NYT) uses our ICON software for reconstructing key goals of the 2022 FIFA World Cup: Technical article (NYT R&D team), Interactive articles for games 1, 2, 3, 4, 5.
Oct 2022: Talk (pptx) at the "Observing and Understanding Hands in Action" workshop at ECCV 2022. Thanks Angela & Linlin for the invite!
Sep 2022: InterCap received the "honorable mention" award at GCPR 2022. Congrats Yinghao et al.!
Aug-Sep 2022: I serve as an Area Chair for BMVC 2022.
July 2022: Open PhD position at UvA (application deadline has passed).
July 2022: Accepted paper at ECCV 2022: SUPR. Congrats Ahmed et al.!
July 2022: Accepted paper at GCPR 2022: InterCap. Congrats Yinghao et al.!
June 2022: SHAPY was a best paper finalist at CVPR 2022 (33 papers shortlisted out of 2064 ones).
June 2022: Joined the University of Amsterdam (Computer Vision group) as an Assistant Professor.
April 2022: Raised 140k EUR from BMBF for the 2022 project "Machine Learning for Interacting Human Avatars" (PS MEWE 103Z (BMBF/Tü AI)).
April 2022: Joined the ELLIS society.
Mar 2022: Accepted papers at CVPR 2022: GOAL (congrats Omid et al.), ICON (congrats Yuliang et al.), SHAPY (congrats Lea and Vassilis et al.) and MOVER (congrats Hongwei et al.).
Oct 2021: Accepted paper at 3DV 2021: PIXIE. Congrats Yao & Vassilis et al.!
Oct 2021: Talk at the University of Bristol, Department of Computer Science.
Sep 2021: Talk at the University of Amsterdam, Informatics Institute.
Aug-Sep 2021: I serve as an Area Chair for 3DV 2021.
June 2021: Talk at Microsot Mixed Reality & AI Lab.
June 2021: We organize the full-day tutorial "SMPL made Simple" at CVPR 2021.
May 2021: Outstanding Reviewer award for CVPR 2021 (top 20.3%).
Mar 2021: Talk at Imperial College London, Intelligent Systems and Networks Group.
Mar 2021: Accepted paper at CVPR 2021: POSA. Congrats Mohamed et al.!
Feb 2021: Talk at Dima Damen's computer vision group (\in VILab, Uni. of Bristol).
Oct 2020: Outstanding Reviewer award for ECCV 2020 (top 7.6%).
Jul 2020: Accepted papers at ECCV 2020: GRAB & ExPose. Congrats Omid et al. and Vassilis et al.!
Jun 2020: Outstanding Reviewer award for CVPR 2020 (top 3.9%).
Jan 2020: Accepted paper at IJCV: "Learning Multi-Human Optical Flow". Congrats Anurag and David et al.!
Sep 2019: Successfully raised 195k EUR from BMBF for the 3-year project "Robust 3D Hand-Object Interaction" (PS MEWE 103Z (BMBF/Tü AI)), for 1 PhD-candidate co-advised with M. J. Black.
Sep 2019: Outstanding Reviewer award for ICCV 2019 (top 3.6%).
Jul 2019: Accepted paper at ICCV 2019: PROX. Congrats Mohamed et al.!
Jul 2019: Accepted paper at GCPR 2019: "Learning to Train with Synthetic Humans". Congrats David et al.!
Mar 2019: Accepted papers at CVPR 2019: ObMan & SMPLify-X. Congrats Yana, George, Vassilis et al.!
Oct 2018: Continuing as Research-Scientist at PS/MPI-IS.
Sep 2018: Accepted paper at SIGA 2017: MANO and SMPL+H. Congrats Javier et al.!
Jan 2017: PhD defense at Uni-Bonn. Thanks Juergen!
Oct 2016: Starting as Post-Doc at PS/MPI-IS.
(last updated: May 2023)
May 2023:
Outstanding Reviewer award for CVPR 2023 (among 232 out of 6625, top 3.5%).
Feb 2023:
- Accepted papers at CVPR 2023:
- "Detecting Human-Object Contact in Images"
Yixin Chen, Sai Kumar Dwivedi, Michael J. Black, Dimitrios Tzionas
Project Website (HOT)
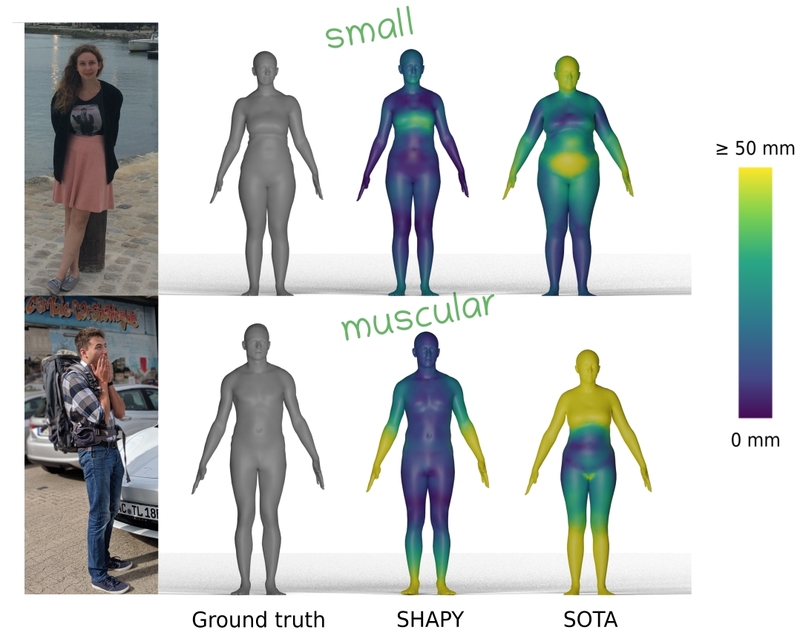
- "3D Human Pose Estimation via Intuitive Physics"
Shashank Tripathi, Lea Müller, Chun-Hao Paul Huang, Omid Taheri, Michael J. Black, Dimitrios Tzionas
Project Website (IPMAN)
- "ECON: Explicit Clothed humans Obtained from Normals"
Yuliang Xiu, Jinlong Yang, Xu Cao, Dimitrios Tzionas, Michael J. Black
Project Website (ECON)
- "ARCTIC: A Dataset for Dexterous Bimanual Hand-Object Manipulation"
Zicong Fan, Omid Taheri, Dimitrios Tzionas, Muhammed Kocabas, Manuel Kaufmann, Michael J. Black, Otmar Hilliges
Project Website (ARCTIC)
- "Reconstructing Signing Avatars From Video Using Linguistic Priors"
Maria-Paola Forte, Peter Kulits, Chun-Hao Paul Huang, Vasileios Choutas, Dimitrios Tzionas, Katherine J. Kuchenbecker, Michael J. Black
Project Website (SGNify)
- "Detecting Human-Object Contact in Images"
July 2022:
Open PhD positionat UvA (application deadline has passed)- Accepted paper at GCPR 2022:
- "InterCap: Joint Markerless 3D Tracking of Humans and Objects in Interaction"
Yinghao Huang, Omid Taheri, Michael J. Black, Dimitrios Tzionas
Project website
- "InterCap: Joint Markerless 3D Tracking of Humans and Objects in Interaction"
- Accepted paper at ECCV 2022:
- "SUPR: A Sparse Unified Part-Based Human Body Model"
Ahmed A. A. Osman, Timo Bolkart, Dimitrios Tzionas, and Michael J. Black
Project website
- "SUPR: A Sparse Unified Part-Based Human Body Model"
June 2022:
- Joined the University of Amsterdam (Computer Vision group) as an Assistant Professor.
- SHAPY was a best paper finalist at CVPR 2022 (33 papers shortlisted out of 2064 ones).
April 2022:
- Successfully raised 140k EUR from BMBF for the 2022 project "Machine Learning for Interacting Human Avatars" (PS MEWE 103Z (BMBF/Tü AI)). Used for 1 senior researcher (PI) and 1 PhD student, both for 12 months.
Mar 2022:
- Joined the ELLIS society.
Mar 2022:
- Accepted papers at CVPR 2022:
- "GOAL: Generating 4D Whole-Body Motion for Hand-Object Grasping"
Omid Taheri, Vasileios Choutas, Michael J. Black, Dimitrios Tzionas
Project Website - "ICON: Implicit Clothed humans Obtained from Normals"
Yuliang Xiu, Jinlong Yang, Dimitrios Tzionas, Michael J. Black
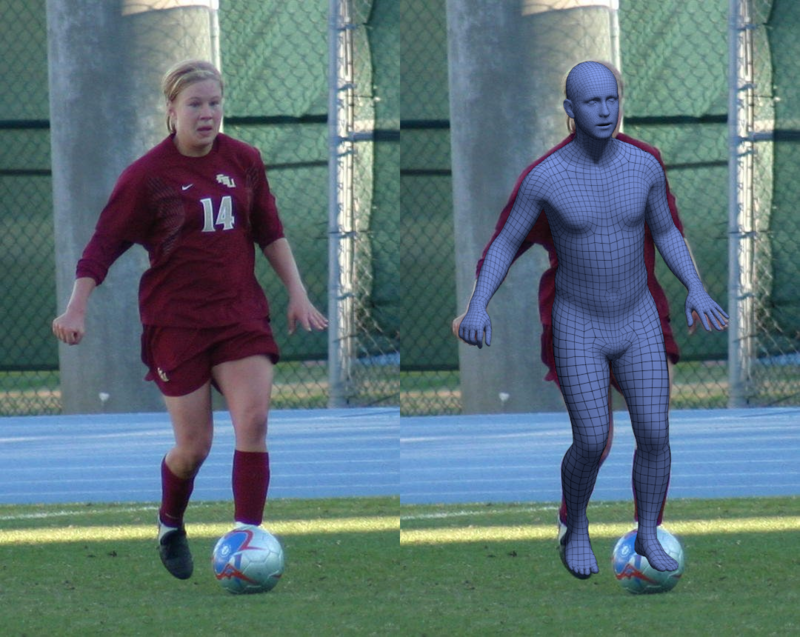
Project Website - "Accurate 3D Body Shape Regression using Metric and Semantic Attributes"
Vasileios Choutas*, Lea Müller*, Chun-Hao Paul Huang, Siyu Tang, Dimitrios Tzionas and Michael J. Black
Project Website - "Human-Aware Object Placement for Visual Environment Reconstruction"
Hongwei Yi, Chun-Hao P. Huang, Dimitrios Tzionas, Muhammed Kocabas, Mohamed Hassan, Siyu Tang, Justus Thies, Michael J. Black
Project Website
- "GOAL: Generating 4D Whole-Body Motion for Hand-Object Grasping"
Oct 2021:
- Talk at the University of Bristol, Department of Computer Science.
Sep 2021:
-
Talk at the University of Amsterdam, Informatics Institute.
Aug-Sep 2021:
-
I serve as an Area Chair for 3DV 2021.
June 2021:
-
We will organize the full-day tutorial "SMPL made Simple" at CVPR 2021.
-
Talk at Microsot Mixed Reality & AI Lab.
May 2021:
Outstanding Reviewer for CVPR 2021 (top 20.3%).
Mar 2021:
- Talk at Imperial College London, Intelligent Systems and Networks Group.
- Accepted paper at CVPR 2021:
- "Populating 3D Scenes by Learning Human-Scene Interaction"
Mohamed Hassan, Partha Ghosh, Joachim Tesch, Dimitrios Tzionas, Michael J. Black
Project Website
- "Populating 3D Scenes by Learning Human-Scene Interaction"
Feb 2021:
- Talk at Dima Damen's computer vision group (\in VILab, Uni. of Bristol) - Feb 16th.
Oct 2020
Outstanding Reviewer award for ECCV 2020 (among 214 out of 2830, top 7.6%).
Thanks to Omid Taheri, Muhammed Kocabas, and Nikos Kolotouros for co-reviewing with me 1 paper each.
July 2020
Accepted papers at ECCV 2020:
- "GRAB: A Dataset of Whole-Body Human Grasping of Objects Constrains"
Omid Taheri, Nima Ghorbani, Michael J. Black, Dimitrios Tzionas
Project Website
- "Monocular Expressive Body Regression through Body-Driven Attention"
Vasileios Choutas, Georgios Pavlakos, Timo Bolkart, Dimitrios Tzionas, Michael J. Black
Project Website
June 2020
Outstanding Reviewer award for CVPR 2020 (among 142 out of 3664, top 3.9%).
Thanks to Omid Taheri, Mohamed Hassan, and Muhammed Kocabas for co-reviewing with me 1 paper each.
January 2020
Accepted paper at International Journal of Computer Vision:
- "Learning Multi-Human Optical Flow"
Anurag Ranjan*, David T. Hoffmann*, Dimitrios Tzionas, Siyu Tang, Javier Romero, Michael J. Black
Project Website
September 2019
Outstanding Reviewer award for ICCV 2019 (among 91 out of 2506, top 3.6%).
Thanks to Vassilis Choutas and Mohamed Hassan for co-reviewing with me 2 papers each.
July 2019
Accepted paper at ICCV 2019:
- "Resolving 3D Human Pose Ambiguities with 3D Scene Constrains"
Mohamed Hassan, Vasileios Choutas, Dimitrios Tzionas, Michael J. Black
Project Website
Accepted paper at GCPR 2019:
- "Learning to Train with Synthetic Humans"
David Hoffmann, Dimitrios Tzionas, Michael J. Black and Siyu Tang
Project Website
March 2019
Accepted papers at CVPR 2019:
- "Learning Joint Reconstruction of Hands and Manipulated Objects"
Yana Hasson, Gül Varol, Dimitrios Tzionas, Igor Kalevatykh, Michael J. Black, Ivan Laptev, and Cordelia Schmid
Project Website
- "Expressive Body Capture: 3D Hands, Face, and Body from a Single Image"
Georgios Pavlakos, Vasileios Choutas, Nima Ghorbani, Timo Bolkart, Ahmed Osman, Dimitrios Tzionas, and Michael J. Black
Project Website
November 2017
The dataset and models for our paper "Embodied Hands: Modeling and Capturing Hands and Bodies Together" is now online.
September 2017
Our paper "Embodied Hands: Modeling and Capturing Hands and Bodies Together" is accepted at SIGGRAPH-Asia 2017. Project's website.
January 2017
PhD thesis defended @ Uni-Bonn.
August 2016
PhD thesis submitted @ Uni-Bonn.
Talk @:
- 04.08.2016 - Perceiving Systems - MPI for IS, hosted bt Prof. M. Black
- 10.08.2016 - Microsoft Research Cambridge
- 12.08.2016 - University of Oxford, hosted by Prof. P. Torr
- 26.08.2016 - Dyson Robotics Lab at Imperial College, hosted by Prof. A. Davison
Our paper "Reconstructing Articulated Rigged Models from RGB-D Videos" is accepted for oral presentation at the ECCV-Workshop on Recovering 6D Object Pose Estimation (R6D). Projet's website here.
June 2016
Talk @:
- 13.06.2016 - Talk at FORTH institute in Heraklion-Greece, hosted by Prof. A. Argyros
- 17.06.2016 - Talk at Max Planck Institute in Saarbruecken-Germany, hosted by Prof. C. Theobalt
February 2016
Our paper "Capturing Hands in Action using Discriminative Salient Points and Physics Simulation" is accepted from the IJCV special issue "Human Activity Understanding from 2D and 3D data". Project's website here.
November 2015
The Dataset, Source-Code and several Videos and Viewers for the ICCV'15 paper have been uploaded at the project's website.
October 2015
Extended abstract for our ICCV'15 paper "3D Object Reconstruction from Hand-Object Interactions" got accepted for a poster presentation at the 1st Workshop on Object Understanding for Interaction.
September 2015
Our paper "3D Object Reconstruction from Hand-Object Interactions" got accepted for a poster presentation at ICCV'15. Project's website here.
October 2014
One paper submitted to IJCV is under review. Project's website here.
July 2014
GCPR Paper "Capturing Hand Motion with an RGB-D Sensor, Fusing a Generative Model with Salient Points" accepted for an oral presentation.
Please visit the Project Page.
October 2013
Together with Abhilash Srikantha and Domik A. Klein and Fahrettin Gökgöz, we organize the exercises of Juergen Gall's Computer Vision lecture at the University of Bonn (Computer Science department)
June 2013
GCPR Paper "A Comparison of Directional Distances for Hand Pose Estimation" accepted for a poster presentation.
Please visit the Project Page.
Education
| May 2012 - Aug 2016. | Ph.D. (Dr. rer. nat.) |
| University of Bonn (3y) & MPI for Intelligent Systems (1y) | |
| Computer Vision Group & Perceiving Systems dpt | |
| Thesis: "Capturing Hand-Object Interaction and Reconstruction of Manipulated Objects" | |
| Supervisor: Juergen Gall | |
| Committee: Juergen Gall, Antonis Argyros, Reinhard Klein, Carsten Urbach | |
| November 2009 | Diploma in Engineering (5 year curriculum - M.Eng. equivalent) |
| Electrical and Computer Engineering | |
| Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece | |
| Thesis: "Adaptive algorithms for marker detection in an image: Application in the field of Augmented Reality" | |
| Supervisor: Hadjileontiadis Leontios | |
Professional Experience
| June 2022 - Present | Assistant Professor |
| University of Amsterdam | |
| Oct 2018 - May 2022 | Research Scientist |
| Oct 2016 - Oct 2018 | Postdoctoral Researcher (with Michael Black) |
| Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems | |
| Perceiving Systems department | |
| May 2012 - Aug 2016 | Research Student (with Juergen Gall) |
| July 2015 - Aug 2016: University of Bonn, Computer Vision Group | |
| May 2012 - June 2013: MPI for Intelligent Systems | |
| Apr. 2011 - July 2011 | Member of the R&D team for the software project |
| Nov. 2009 - June 2010 | "Epione: An Innovative Pain Management Solution" |
| Mentor: Prof. Dr. L. Hadjileontiadis | |
| Members: K.Vrenas, S.Georgoulis, S.Eleftheriadis | |
| Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece | |
| Aug. 2010 - May 2011 | Greek Army (obligatory service) |
| IT services for A' Army Corps (01-05/2011) | |
Awards
| Best-paper finalist for SHAPY at CVPR 2022 (33 papers shortlisted out of 2064 ones). | |
| Honorable Mention award at the DAGM GCPR 2022 conference for InterCap. | |
| Outstanding Reviewer Award: CVPR 2023 (top 3.5%, 232 reviewers shortlisted out of 6625 ones) | |
| CVPR 2021 (top 20.3%, 1065 reviewers shortlisted out of 5246 ones) | |
| ECCV 2020 (top 7.6%, 215 reviewers shortlisted out of 2830 ones) | |
| CVPR 2020 (top 3.9%, 142 reviewers shortlisted out of 3664 ones) | |
| ICCV 2019 (top 3.6%, 91 reviewers shortlisted out of 2506 ones) | |
| For the "Epione: An Innovative Pain management Solution" team project: Participation in the World finals of Microsoft Imagine Cup 2011 in (July 2011, NYC), after getting in the National Finals the 1st (2011) and 2nd (2010) place. Honorary Rector Award (AUTH). Part of the first TEDxThessaloniki 2010. Invited Presentation to Steve Ballmer (8 July 2011, NYC; ~20 selected teams). | |
Review Service
| Conferences | ||||
| CVPR | Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition | 2016, 2019, 2020**, 2021** 2023** |
||
| ICCV | International Conference on Computer Vision | 2019** | ||
| ECCV | European Conference on Computer Vision | 2020** | ||
| ICRA | International Conference on Robotics and Automation | 2017, 2019 | ||
| IROS | International conference on intelligent Robots and Systems | 2017 | ||
| NeurIPS | Neural Information Processing Systems | 2018 | ||
| HRI | ACM/IEEE International Conference on Human-Robot Interaction | 2016 | ||
| IJCAI | International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence | 2019 | ||
| IEEE VR | IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces | 2020 | ||
| ** Outstanding Reviewer award (ICCV'19, CVPR'20, ECCV'20, CVPR'21, CVPR'23) | ||||
| Journals | ||||
| TPAMI | Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence | 2016, 2020 | ||
| RA-L | Robotics and Automation Letters | 2018 | ||
| JVCI | Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation | 2016 | ||
| TOMM | IEEE Transactions on Multimedia | 2015 | ||
| Sensors | Sensors | Open Access Journal from MDPI | 2014 | ||
Talks
| Reconstructing Expressive and Interacting 3D Humans from a single RGB Image | ||
| 10.2021 | University of Bristol, Department of Computer Science | |
| 09.2021 | University of Amsterdam, Informatics Institute | |
| 06.2021 | Microsoft Mixed Reality & AI Lab | |
| 03.2021 | Imperial College London, Intelligent Systems and Networks Group | |
| From Interacting Hands to Expressive and Interacting Humans | ||
| 16.02.21 | University of Bristol, Hosted by Prof. Dima Damen | |
| Capturing Hand-Object Interaction and Reconstruction of Manipulated Objects | ||
| 13.06.16 | FORTH Institute, Hosted by Prof. Antonis Argyros | (link) |
| 17.06.16 | Max Planck Institute, Hosted by Prof. Christian Theobalt | |
| 04.08.16 | Perceiving Systems - MPI for IS, hosted by Prof. Michael J. Black | (link) |
| 10.08.16 | Microsoft Research Cambridge | |
| 12.08.16 | University of Oxford, hosted by Prof. Philip Torr | (link) |
| 26.08.16 | Dyson Robotics Lab at Imperial College, hosted by Prof. Andrew Davison | |
Languages
| Greek | - | Mother Language |
| English | C2 | Certificate Of Proficiency In English, University Of Cambridge |
| German | C1 | Goethe Zertifikat, Goethe Institut |
(last updated: June 2023)
 HBW (CVPR 2022) - "Human Bodies in the Wild" dataset (link)
HBW (CVPR 2022) - "Human Bodies in the Wild" dataset (link)
A dataset of RGB photos taken in the wild, paired with
ground truth 3D whole-body shape.
The dataset contains 35 subjects and a total of 2543 photos.
Each subject the dataset has:
- an expressive 3D SMPL-X human mesh, and
- a high-resolution 3D scan,
in a canonical T-pose, towards shape-focused evaluation.
 GRAB (ECCV 2020) dataset (link)
GRAB (ECCV 2020) dataset (link)
A dataset of 3D whole-body grasps during human-object interaction.
The dataset contains 1.622.459 frames in total. Each one has:
- an expressive 3D SMPL-X human mesh (shaped and posed),
- a 3D rigid object mesh (posed), and
- contact annotations (wherever applicable).
 ExPose (ECCV 2020) dataset (link)
ExPose (ECCV 2020) dataset (link)
A curated dataset that contains 32.617 pairs of:
- an in-the-wild RGB image, and
- an expressive whole-body 3D human reconstruction (SMPL-X).
The dataset can be used to train models that predict expressive 3D
human bodies, from a single RGB image as input, similar to ExPose.
 PROX (ICCV 2019) - data/code (link)
PROX (ICCV 2019) - data/code (link)
Dataset & Code
SMPL-X / SMPLify-X (CVPR 2019) - models/data (link)
Models & Data & Code
ObMan (CVPR 2019) - models/data (link)
Models & Data & Code
SIGGRAPH-Asia 2017 (TOG) models/dataset (link)
Models & Alignments & Scans, for:
- hand-only (MANO)
- body+hand (SMPL+H)
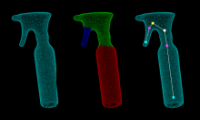 ECCVw 2016 dataset (link)
ECCVw 2016 dataset (link)
RGB-D dataset of an object under manipulation.
The dataset also contains input 3D template meshes
for each object and output articulated models.
 IJCV 2016 dataset (link)
IJCV 2016 dataset (link)
Annotated RGB-D + multicamera-RGB dataset of one or two hands
interacting with each other and/or with a rigid or an articulated object

ICCV 2015 dataset (link)
RGB-D dataset of a hand rotating a rigid object for 3d scanning

GCPR 2014 dataset (link)
Annotated RGB-D dataset of one or two hands interacting with each other

GCPR 2013 dataset (link)
Synthetic dataset of two hands interacting with each other
(last updated: May 2023)
I have been fortunate to enjoy a diverse group of collaborators; as of May 2023 I have-co-authored papers with 54 people from 16 countries and 4 continents, while more people are involved in ongoing work.
Full-Thesis Advising, PhD
| Dimitrije Antic | (PhD) | Mar 2023 - Present | Co-Advised by T. Gevers | 3D human-object interaction from images |
| Sai Kumar Dwivedi | (PhD) | Oct 2021 - Present | Co-Advised by M. Black | 3D human pose and shape from images |
| Yuliang Xiu | (PhD) | Nov 2020 - Present | Co-Advised by M. Black | Creating realistic 3D human avatars for AR/VR |
| Omid Taheri | (PhD) | July 2018 - Present | Co-Advised by M. Black | Capturing and generating whole-body human-object interactions. |
| Vasileios Choutas | (PhD) | May 2018 - Dec 2022 | Co-Advised by M. Black | Regressing 3D expressive and interacting humans from images. |
Advising for Series of Projects, PhD
| Shashank Tripathi | (PhD) | 2021 - Present | Physics-inspired human pose estimation |
| Mohamed Hassan | (PhD) | 2018 - 2021 | Capturing & generating Human-Scene Interactions (HSI) |
MSc thesis
| Romana Wilschut | (MSc) | UvA | Oct 2022 - Aug 2023 | Controllable 3D hand-grasp generation | |
| David Hoffmann | (MSc) | Uni-Tue | Jan 2018 - Jan 2019 | Co-Advised by S. Tang | MSc thesis. Papers: GCPR'19, IJCV'20. Next: PhD at Uni-Freiburg & Bosch |
BSc thesis (UvA)
| Benjamin van Altena | (BSc) | UvA | April - Aug 2023 | 3D Human reconstruction from a single color image |
| Roan van Blanken | (BSc) | UvA | April - Aug 2023 | 3D Human reconstruction from a single color image |
GRAB: A Dataset of Whole-Body Human Grasping of Objects
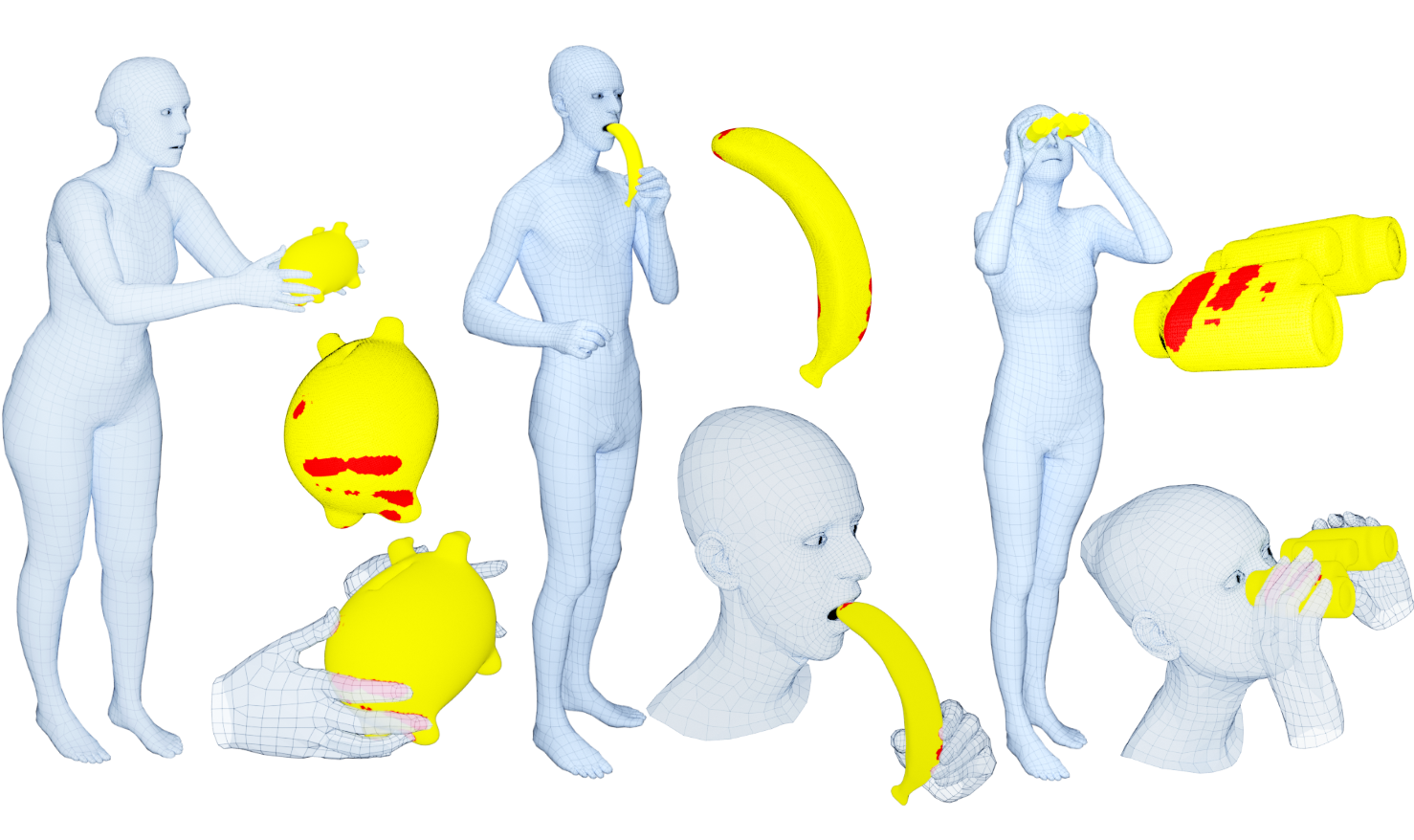
Training computers to understand, model, and synthesize human grasping requires a rich dataset containing complex 3D object shapes, detailed contact information, hand pose and shape, and the 3D body motion over time. While "grasping" is commonly thought of as a single hand stably lifting an object, we capture the motion of the entire body and adopt the generalized notion of "whole-body grasps". Thus, we collect a new dataset, called GRAB (GRasping Actions with Bodies), of whole-body grasps, containing full 3D shape and pose sequences of 10 subjects interacting with 51 everyday objects of varying shape and size. Given MoCap markers, we fit the full 3D body shape and pose, including the articulated face and hands, as well as the 3D object pose. This gives detailed 3D meshes over time, from which we compute contact between the body and object. This is a unique dataset, that goes well beyond existing ones for modeling and understanding how humans grasp and manipulate objects, how their full body is involved, and how interaction varies with the task. We illustrate the practical value of GRAB with an example application; we train GrabNet, a conditional generative network, to predict 3D hand grasps for unseen 3D object shapes. The dataset and code are available for research purposes at https://grab.is.tue.mpg.de.
Monocular Expressive Body Regression through Body-Driven Attention
To understand how people look, interact, or perform tasks,we need to quickly and accurately capture their 3D body, face, and hands together from an RGB image. Most existing methods focus only on parts of the body. A few recent approaches reconstruct full expressive 3D humans from images using 3D body models that include the face and hands. These methods are optimization-based and thus slow, prone to local optima, and require 2D keypoints as input. We address these limitations by introducing ExPose (EXpressive POse and Shape rEgression), which directly regresses the body, face, and hands, in SMPL-X format, from an RGB image. This is a hard problem due to the high dimensionality of the body and the lack of expressive training data. Additionally, hands and faces are much smaller than the body, occupying very few image pixels. This makes hand and face estimation hard when body images are downscaled for neural networks. We make three main contributions. First, we account for the lack of training data by curating a dataset of SMPL-X fits on in-the-wild images. Second, we observe that body estimation localizes the face and hands reasonably well. We introduce body-driven attention for face and hand regions in the original image to extract higher-resolution crops that are fed to dedicated refinement modules. Third, these modules exploit part-specific knowledge from existing face and hand-only datasets. ExPose estimates expressive 3D humans more accurately than existing optimization methods at a small fraction of the computational cost. Our data, model and code are available for research at https://expose.is.tue.mpg.de.
Expressive Body Capture: 3D Hands, Face, and Body from a Single Image
To facilitate the analysis of human actions, interactions and emotions, we compute a 3D model of human body pose, hand pose, and facial expression from a single monocular image. To achieve this, we use thousands of 3D scans to train a new, unified, 3D model of the human body, SMPL-X, that extends SMPL with fully articulated hands and an expressive face. Learning to regress the parameters of SMPL-X directly from images is challenging without paired images and 3D ground truth. Consequently, we follow the approach of SMPLify, which estimates 2D features and then optimizes model parameters to fit the features. We improve on SMPLify in several significant ways: (1) we detect 2D features corresponding to the face, hands, and feet and fit the full SMPL-X model to these; (2) we train a new neural network pose prior using a large MoCap dataset; (3) we define a new interpenetration penalty that is both fast and accurate; (4) we automatically detect gender and the appropriate body models (male, female, or neutral); (5) our PyTorch implementation achieves a speedup of more than 8x over Chumpy. We use the new method, SMPLify-X, to fit SMPL-X to both controlled images and images in the wild. We evaluate 3D accuracy on a new curated dataset comprising 100 images with pseudo ground-truth. This is a step towards automatic expressive human capture from monocular RGB data. The models, code, and data are available for research purposes at https://smpl-x.is.tue.mpg.de.
Embodied Hands: Modeling and Capturing Hands and Bodies Together
Humans move their hands and bodies together to communicate and solve tasks. Capturing and replicating such coordinated activity is critical for virtual characters that behave realistically. Surprisingly, most methods treat the 3D modeling and tracking of bodies and hands separately. Here we formulate a model of hands and bodies interacting together and fit it to full-body 4D sequences. When scanning or capturing the full body in 3D, hands are small and often partially occluded, making their shape and pose hard to recover. To cope with low-resolution, occlusion, and noise, we develop a new model called MANO (hand Model with Articulated and Non-rigid defOrmations). MANO is learned from around 1000 high-resolution 3D scans of hands of 31 subjects in a wide variety of hand poses. The model is realistic, low-dimensional, captures non-rigid shape changes with pose, is compatible with standard graphics packages, and can fit any human hand. MANO provides a compact mapping from hand poses to pose blend shape corrections and a linear manifold of pose synergies. We attach MANO to a standard parameterized 3D body shape model (SMPL), resulting in a fully articulated body and hand model (SMPL+H). We illustrate SMPL+H by fitting complex, natural, activities of subjects captured with a 4D scanner. The fitting is fully automatic and results in full body models that move naturally with detailed hand motions and a realism not seen before in full body performance capture. The models and data are freely available for research purposes at http://mano.is.tue.mpg.de.
Reconstructing Articulated Rigged Models from RGB-D Videos
Although commercial and open-source software exist to reconstruct a static object from a sequence recorded with an RGB-D sensor, there is a lack of tools that build rigged models of articulated objects that deform realistically and can be used for tracking or animation. In this work, we fill this gap and propose a method that creates a fully rigged model of an articulated object from depth data of a single sensor. To this end, we combine deformable mesh tracking, motion segmentation based on spectral clustering and skeletonization based on mean curvature flow. The fully rigged model then consists of a watertight mesh, embedded skeleton, and skinning weights.
Capturing Hands in Action using Discriminative Salient Points and Physics Simulation
Hand motion capture is a popular research field, recently gaining more attention due to the ubiquity of RGB-D sensors. However, even most recent approaches focus on the case of a single isolated hand. In this work, we focus on hands that interact with other hands or objects and present a framework that successfully captures motion in such interaction scenarios for both rigid and articulated objects. Our framework combines a generative model with discriminatively trained salient points to achieve a low tracking error and with collision detection and physics simulation to achieve physically plausible estimates even in case of occlusions and missing visual data. Since all components are unified in a single objective function which is almost everywhere differentiable, it can be optimized with standard optimization techniques. Our approach works for monocular RGB-D sequences as well as setups with multiple synchronized RGB cameras. For a qualitative and quantitative evaluation, we captured 29 sequences with a large variety of interactions and up to 150 degrees of freedom.
3D Object Reconstruction from Hand-Object Interactions
Recent advances have enabled 3d object reconstruction approaches using a single off-the-shelf RGB-D camera. Although these approaches are successful for a wide range of object classes, they rely on stable and distinctive geometric or texture features. Many objects like mechanical parts, toys, household or decorative articles, however, are textureless and characterized by minimalistic shapes that are simple and symmetric. Existing in-hand scanning systems and 3d reconstruction techniques fail for such symmetric objects in the absence of highly distinctive features. In this work, we show that extracting 3d hand motion for in-hand scanning effectively facilitates the reconstruction of even featureless and highly symmetric objects and we present an approach that fuses the rich additional information of hands into a 3d reconstruction pipeline, significantly contributing to the state-of-the-art of in-hand scanning.
Capturing Hand Motion with an RGB-D Sensor, Fusing a Generative Model with Salient Points
Hand motion capture has been an active research topic in recent years, following the success of full-body pose tracking. Despite similarities, hand tracking proves to be more challenging, characterized by a higher dimensionality, severe occlusions and self-similarity between fingers. For this reason, most approaches rely on strong assumptions, like hands in isolation or expensive multi-camera systems, that limit the practical use. In this work, we propose a framework for hand tracking that can capture the motion of two interacting hands using only a single, inexpensive RGB-D camera. Our approach combines a generative model with collision detection and discriminatively learned salient points. We quantitatively evaluate our approach on 14 new sequences with challenging interactions.
A Comparison of Directional Distances for Hand Pose Estimation
Benchmarking methods for 3d hand tracking is still an open problem due to the difficulty of acquiring ground truth data. We introduce a new dataset and benchmarking protocol that is insensitive to the accumulative error of other protocols. To this end, we create testing frame pairs of increasing difficulty and measure the pose estimation error separately for each of them. This approach gives new insights and allows to accurately study the performance of each feature or method without employing a full tracking pipeline. Following this protocol, we evaluate various directional distances in the context of silhouette-based 3d hand tracking, expressed as special cases of a generalized Chamfer distance form. An appropriate parameter setup is proposed for each of them, and a comparative study reveals the best performing method in this context.